
Evolution of AI Language Models: From GPT to DeepSeek and Qwen – Applications and Future Directions
- [printfriendly]
The rapid advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) has led to the development of sophisticated large language models (LLMs) that are transforming industries, education, and human-computer interaction. This evolution has progressed through multiple generations of AI models, starting with early rule-based systems, followed by statistical models, deep learning-based transformers, and now highly advanced models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT, DeepSeek’s DeepSeek-V3, and Alibaba’s Qwen. While ChatGPT has dominated the conversational AI space, emerging models such as DeepSeek and Qwen offer competitive alternatives with open-weight architectures and specialized multilingual capabilities. This paper provides an overview of the evolution of AI language models, their technical distinctions, potential applications, and future research directions toward next-generation AI systems.
I. Introduction
The field of artificial intelligence has undergone a dramatic transformation with the rise of large language models (LLMs). Early AI systems relied on rule-based and statistical methods, but the introduction of deep learning and transformer architectures enabled the development of highly capable models like OpenAI’s GPT-3 (2020), which marked a turning point in natural language processing (NLP). Subsequent advancements led to ChatGPT (2022), which introduced conversational AI to the mainstream, followed by GPT-4 (2023), which improved reasoning, reduced biases, and integrated multimodal capabilities.
Parallel developments include DeepSeek-V3 (2024), an open-weight model optimized for long-context understanding and coding tasks, and Qwen (2023), Alibaba’s bilingual (Chinese-English) AI with strong multimodal applications. These models differ in architecture, accessibility, and regional adoption, shaping the future of AI deployment across industries.
This paper explores the evolution of AI language models, comparing their technical capabilities, societal impact, and future research directions toward more advanced AI systems.
II. Early AI Language Models (Pre-Transformer Era)
Before the advent of modern LLMs, AI language processing relied on:
- Rule-Based Systems (1960s-1980s): Handcrafted linguistic rules (e.g., ELIZA).
- Statistical Models (1990s-2000s): Probabilistic approaches like Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) and n-grams.
- Neural Networks (2010s): Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks improved context retention but struggled with long-range dependencies.
The Transformer architecture (2017) revolutionized NLP by enabling parallel processing and attention mechanisms, paving the way for models like BERT (2018) and GPT (2018).
III. The Rise of Modern LLMs: GPT-3 to ChatGPT
A. GPT-3 (2020)
- Parameters: 175 billion
- Capabilities: Few-shot learning, text generation, basic reasoning.
- Limitations: Hallucinations, lack of real-time knowledge updates.
B. ChatGPT (GPT-3.5 & GPT-4, 2022-2023)
- Key Advancements:
- Fine-tuned for conversational fluency.
- GPT-4 introduced multimodal (text + image) processing.
- Integrated into Microsoft’s ecosystem (Copilot, Bing AI).
- Impact:
- Revolutionized customer service, education, and content creation.
- Raised ethical concerns about misinformation and job displacement.
IV. Emerging Competitors: DeepSeek and Qwen
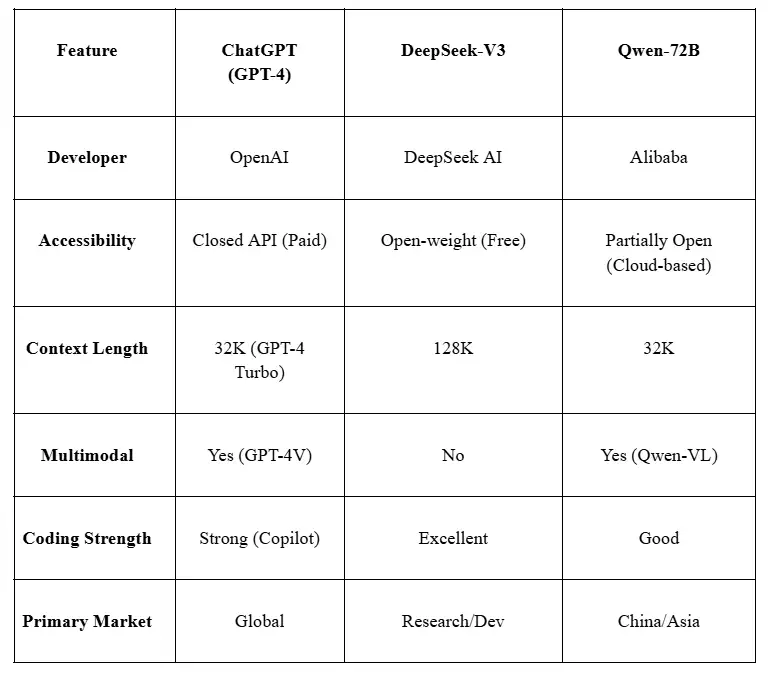
A. DeepSeek-V3 (2024)
- Key Features:
- 128K context window (superior for long-document analysis).
- Open-weight model, enabling fine-tuning and research flexibility.
- Strong in coding & math, competing with GPT-4 in technical tasks.
- Applications:
- Research, software development, legal document analysis.
B. Qwen (Alibaba, 2023)
- Key Features:
- Bilingual (Chinese-English) optimization.
- Multimodal (Qwen-VL) for image-text tasks.
- Integrated into Alibaba Cloud for enterprise AI.
- Applications:
- E-commerce, cloud computing, government AI services in China.
V. Comparative Analysis
VI. Future Directions & Challenges
A. Next-Gen AI (Beyond GPT-4, DeepSeek, Qwen)
- Agentic AI: Autonomous AI agents performing complex workflows.
- Real-Time Learning: Continuous knowledge updates without retraining.
- Regulatory Challenges: Global AI governance, bias mitigation.
B. Societal Impact
- Job Market Shifts: AI-assisted roles vs. displacement risks.
- Education: AI tutors, personalized learning.
- Ethics: Deepfakes, misinformation, and AI accountability.
VII. Conclusion
The evolution of AI language models—from early statistical methods to ChatGPT, DeepSeek, and Qwen—demonstrates rapid advancements in NLP. While ChatGPT leads in conversational AI, DeepSeek offers transparency for researchers, and Qwen dominates in Chinese-language applications. Future developments will focus on real-time learning, multimodal reasoning, and ethical AI deployment, shaping the next generation of intelligent systems.
References
- OpenAI. (2023). GPT-4 Technical Report.
- DeepSeek AI. (2024). DeepSeek-V3: A Long-Context Open Language Model.
- Alibaba. (2023). Qwen: Bridging Multilingual and Multimodal AI.
- Bubeck, S., et al. (2023). "Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4." Microsoft Research.



